Ecuador - El Pais
|
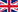
Ecuador es uno de los más pequeños en América del Sur, está atrevesado por la línea Ecuador (de donde toma su nombre) que lo divide en dos hemisferios, limite al norte con Colombia, al sur y al este con Perú al oeste con el Océano Pacífico. |
 |
|
Con este territorio relativamente pequeño, Ecuador tiene la mayor biodiversidad por área en el Mundo. En un estudio de Conservación Internacional, Ecuador está considerado entre los 17 países más "Megadiversos" entre ellos están: E.E.U.U, China, Australia, Brasil México. Con 9.2 especies por km2, este ocupa el primer lugar en el mundo con referencia a las especies por área.
La riqueza de este país se basa en su diversidad tanto natural como cultural por eso catalogado uno de las países más megadiversos del mundo.
Ecuador tiene 4 regiones naturales: La Selva, La Costa, La Sierra y Las Islas Galápagos o archipiélago de Galápagos. Estas cuatro regiones se subdividen en 24 provincias, además de su exuberante biodiversidad, Ecuador tiene una impresionante variedad de grupos étnicos, incluyendo algunas comunidades que todavia mantienen sus manifestaciones culturales ancestrales.
|
|
Información
| Capital: | Quito |
| Gobierno: | República |
| Moneda: | 1 US-Dollar (USD) = 100 Centavos |
| Superficie: | 284.000 km² |
| Población: | 14,2 Millones (growth rate: 2.1%) |
| Idiomas oficiales: | Español y Quichua |
| Religion: | Católica 95 % |
| Código de pais (phone): | +593 |
| Tempo zona: | MEZ-6h |
| Gobierno: | Democrático |
| Presidente: | Rafael Correa |
| GDP: | US$ 58.7 billion (US$ 2'910 p. person) |
| Poder Legislativo: | Asamblea Nacional con 130 curules |
| Independencia: | Primer grito 10 de Agosto de 1809 y la Independencia Total el 24 de Mayo de 1822 |
| Relaciones comerciales: | US, Latino America, Europa, Asia El Caribe |
| Industria: | Petróleo, banana, camarones, pescado, café, textiles,oro, plata, papel, madera, químicos, plasticos, pesca, madera. |
La Costa

Las provincias en la región Costa son:
Esmeraldas, Manabí, Guayas, Santa Elena, Los Ríos y El Oro.
La Sierra (Los Andes)

Las provincias de la Sierra son: Carchi, Imbabura, Pichincha, Santo Domingo de los Tzáchilas, Cotopaxi, Tungurahua, Bolívar, Chimborazo, Cañar, Azuay y Loja.
El Oriente (La Amazonía)

Las provincias de esta región son: Sucumbios, Napo, Orellana, Pastaza, Morona Santiago y Zamora Chinchipe.
Las Islas Galápagos

The Galapagos islands (official name Archipiélago de Colón) is a group of islands in the pacific and belong to Ecuador. In total 13 bigger islands (Santiago, Santa Cruz, Floreana , San Cristóbal, Española, Genovesa, Santa Fe, Isabela, Fernandina, Darwin, Roca Redonda, Marchena, Pinta), 8 small islands and approximattly 40 "mini-islands" belong to this national reserve. 2001, approximatly 18'500 people lived on those islands.
The Flora and Fauna on these islands is fabulouse and if you are in Ecuador it is a must to visit these islands.
The climate
Ecuador is located in the Tropical Zone, thus, the climate throughout the country ranges from tropical equatorial rainy weather to perpetual snow on the top of the mountains due to the influence of the Andean Mountain range in the highlands. Cities in the highlands have temperatures that vary from 10 to 22 °C, while coastal cities’ temperatures vary from 15 to 28°C during the day. The jungle has constant weather conditions: rainy, humid and warm. The Galapagos Islands are always sunny and warm. Temperature drops a bit during the months of June to November.
- Quito and Highlands. Wear spring attire during June, July and August. During the rest of the months, bring warmer clothing like those you would wear during the fall. A raincoat or jacket would be useful at night since it gets pretty chilly.
- Guayaquil and other coastal cities: wear summer clothing all year round. During the rainy months, December to May, the weather is still very warm. During the months of June to November the weather is cloudy and a little bit colder.
- Galapagos: wear comfortable walking shoes and casual clothing. Shorts, t-shirts and summer clothing will be just tine. Don’t forget a hat and sun block as they are a must along with a bathing suit.
- Amazon or Jungle: wear clothing adequate for a rainy season. If you can get yourself a raincoat, take it with you, as well as several sets of light pants and long sleeves shirts. Shorts are less useful because of the insects and abundant vegetation you will walk through on your excursions. Rubber boots and insect repellents are necessary to take along with a hat. If you plan to take pictures, you will need high speed film.
Health risks
No innoculations are required for entry. However, it is reccomended to get vaccinations for hepatitis A and B, typhoid, and there is a minor risk of cholera and rabies. It is strongly recommended to get a yellow fever vaccination if you plan to visit the rainforest during rainy season. Please consult your doctor for further informaition.
HistoryOrigin of the Ecuadorian people.
According to different scientist and historians, large groups of people from Asia crossed the Bering Strait eventually reaching the South American continent and settled down. Archaeological evidence found in the small village of Punin (South of Riobamba) shows that this settlement period lasted several hundred years.
ECUADORIAN PREHISTORY.
The Ecuadorian prehistory can de divided as following:
PRE-CERAMIC (approximately 9000 years B.C.)
Evidence from this period was found in 1959 in and around Inga.
FORMATIVE (3000 to 1500 years B.C.)
The most representative culture of this period was the “Valdivia”. This tribe is very well known for its ceramic works, specially small female figurines depicting their goddesses or events of daily life.
MIDDLE FORMATIVE (2000 - 1300 years B.C.)
During the latter part of the “Valdivia” culture new cultures appeared. The most important, “Machalilla”, was more advanced than the Valdivia.
LATER FORMATIVE (1500-500 B.C.)
The only culture discovered from this period is the “Chorrera”. This culture experimented with a different way of painting using honey to create new textures and colours. This tribal group is known for their fine ceramics, very similar to porcelain.
REGIONAL DEVELOPMENT (500 years B.C.)
The tribes that lived during this period of time were farmers, fishermen, and craftsmen. These societies had very marked social divisions with the priests acting as the rules. This tribe constructed temples of polished and caved stones.
INTEGRATION CULTURES ( 200 B.C. and A.D.)
The tribes during this time are viewed as independent nations, each one having its own government. Eventually, they formed an alliance known as the Reino de Quito. This federation occurred when it became necessary for them to fight against the Inca invaders.
THE QUITUS KINGDOM
Quito was used by the first Spaniards, who took this name form the Indians. Quito not only applied to a single place, but also to a region and latter to the territory Known as Real Audiencia de Quito during the colonial time. The name of this Spanish colonial territory was changed to Ecuador when the Republic was formed.
The Quitus Kingdom lasted from about 980 to 1450 years A.C and was one of the largest and most developed nations of this area.
THE INCA EMPIRE
The Inca Tupac-Yupanqui was in charge of the conquest from Cuzco, He founded Tomebamba in Cañari territory. There he built palaces and temples like: Pumapungo, Ingapirca, and Tambo Blanco. During this time he fathered a son, Huayna Capac, by a Cañari Princess. Tupac-Yupanqui returned to Cuzco where he died and his son became the new Inca King.
Huayna-Capac continued the invasion. In Quito he knew Paccha with who had a son Atahualpa, who was his favourite son and the last Inca. The Inca Empire, divided by political and racial hatred became weaker, and even when Atahualpa defeated Huáscar; it was not possible to unify the Kingdom again. Due to these circumstances, it was easy for Spaniards ton conquer the great Tahuantinsuyo.
THE SPANISH CONQUEST
Francisco Pizarro arrived in the Incan Empire in Septembre 1532 on a exploratory mission. Pizarro arranged a meeting with Atahualpa. It was held in Cajamarca (Perú) on November 1532. Once Atahualpa and his retinue were at the meeting place, the Spanish Conquistadors massacred most of Atahualpa’s people and captured him. Atahualpa was condemned and executed on August 29, 1533.
One of Atahualpa’s generals, Rumiñahui, continued fighting against the traitors for about two more years. Finally , Pizarro’s lieutenant Sebastian de Benalcázar defeated Rumiñahui “Face of stone” in late 1534.
THE COLONIAL ERA
The colonial period lasted 274 years from 1533 to August 10 of 1809. During this time Ecuador remained a peaceful colony. The Spanish founded several villages that were named for Spanish regions or cities.
INDEPENDENCE
The living conditions generated great discontent among them. The cruelty and abuse of the rich colonialists were reasons enough for several uprising during the Colonial Period.
The first serious attempt was made on August 10, 1809 in Quito. A group of patriots formed by well-known lawyers and writers. The preceding night, they resolved to replace the tyrannical Spanish authorities with a patriotic group called the Sovereign Board led by the Marquis of Selva Alegre and Juan Pío Montúfar.
THE REPUBLIC
The same day that Ecuador made its separation from Gran Colombia the main civil, military and religious authorities met together declare Ecuador as a sovereign independent nation. General Juan José Flores was in charge of the government.
On August 10, 1830, General Flores convened the Congress that created the first Ecuadorian Constitution. In this legal document Quito was declared capital o the, new republic. The Constitution promulgated laws in favour of democracy and elections.